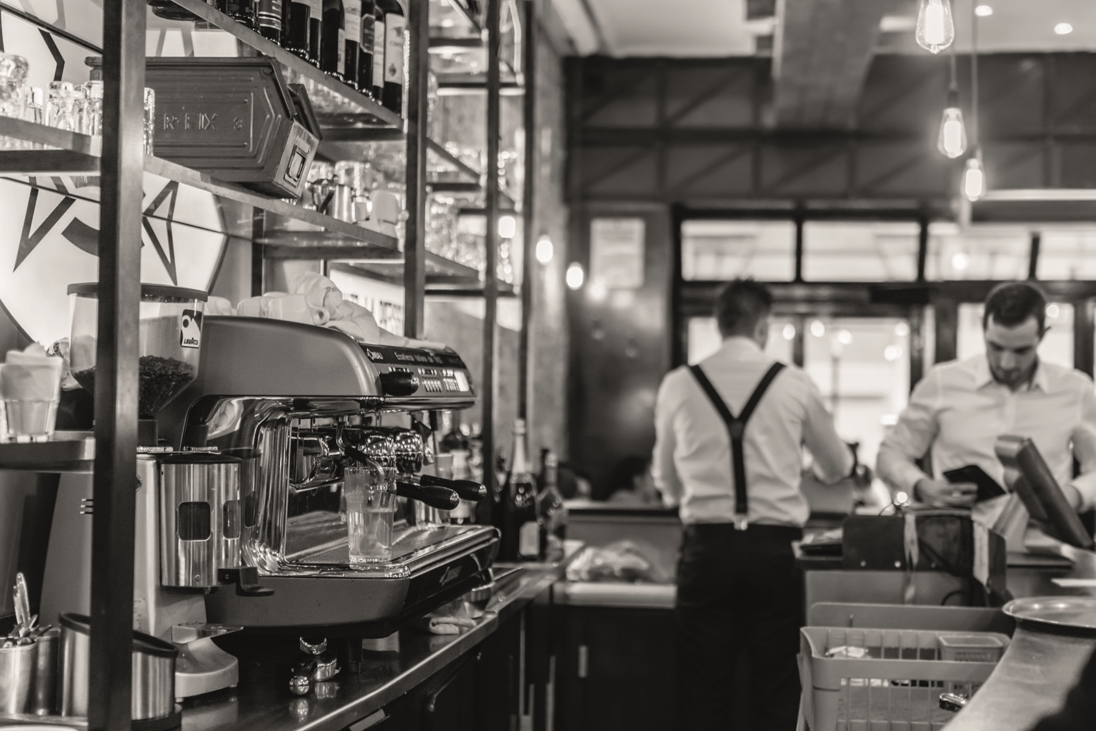
Distributed audio systems have become indispensable tools in commercial applications, offering businesses unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and performance. These systems allow audio to be distributed across multiple zones or areas within a facility, providing seamless coverage and control over sound reinforcement. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of distributed audio systems in commercial applications, along with key design considerations, installation tips, and best practices for achieving seamless integration and optimal performance.
Benefits of Distributed Audio Systems:
Distributed audio systems offer a myriad of benefits for commercial applications:
- Flexibility: Distributed audio systems allow businesses to customise audio experiences for different zones or areas within a facility. Whether it’s background music in retail spaces, paging announcements in office buildings, or immersive soundscapes in hospitality venues, distributed audio systems offer the flexibility to tailor audio content to specific requirements.
- Scalability: Distributed audio systems can easily scale to accommodate the evolving needs of a business. Whether expanding to additional zones or integrating with other audiovisual systems, distributed audio systems offer scalability without compromising performance or reliability.
- Centralised Control: Distributed audio systems centralise control and management, allowing businesses to adjust volume levels, audio sources, and schedule playlists from a single interface for the whole venue or per each individual zone. This centralised approach simplifies operation and provides the opportunity to deliver a personalised experience, especially in multi-zone environments.
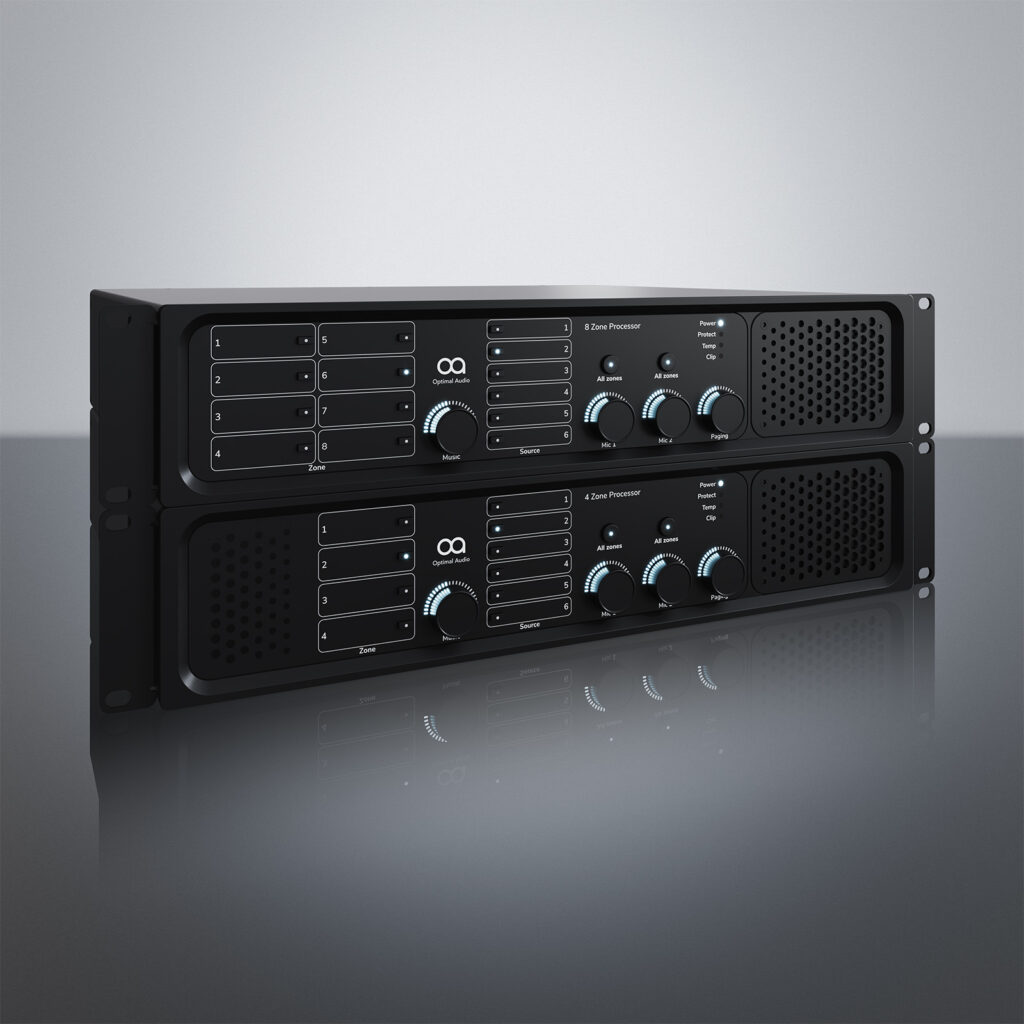
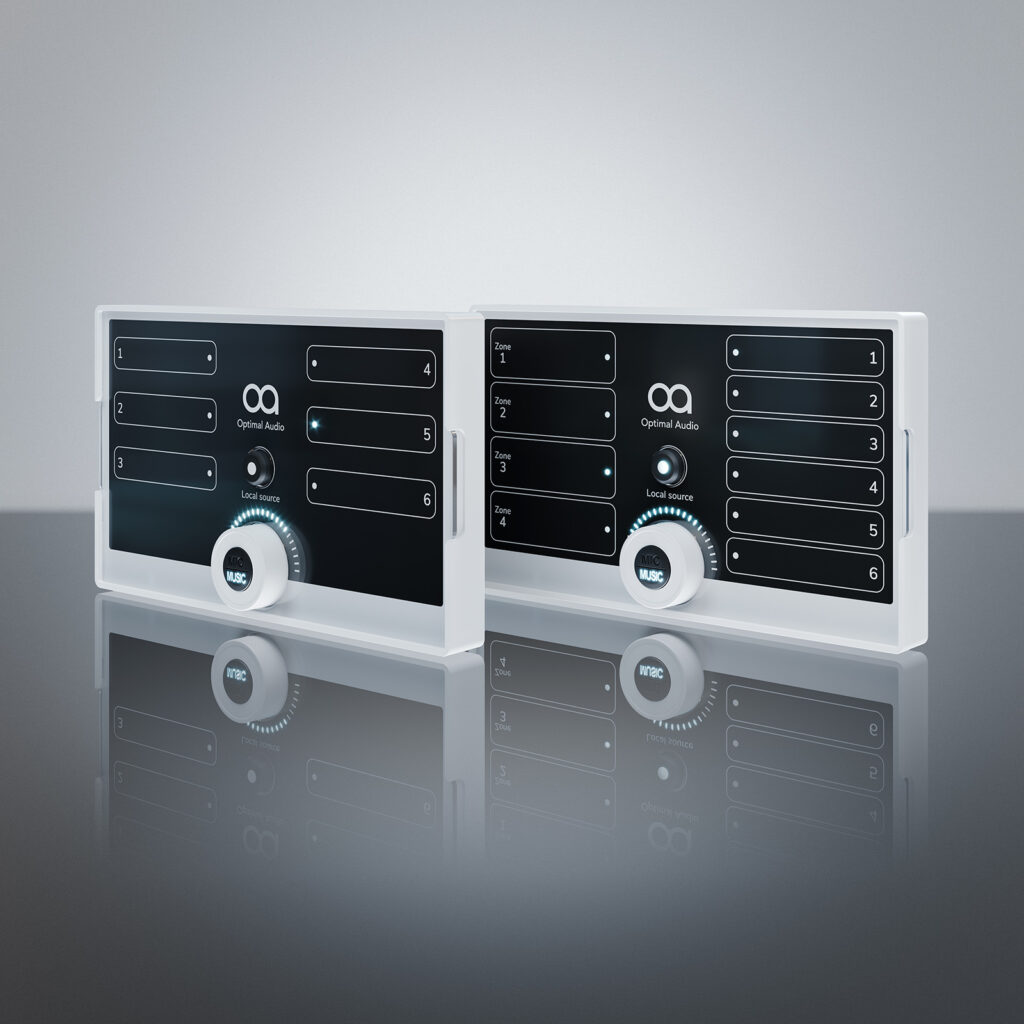


Design Considerations:
When designing a distributed audio system for commercial applications, several key considerations should be taken into account:
- Zone Layout and Coverage: Carefully assess the layout and usage patterns of the facility to determine the optimal placement of audio zones and speakers. Consider factors such as room dimensions, acoustics, and ambient noise levels when defining zone boundaries and speaker placements to ensure uniform coverage and optimal sound quality.
- Audio Source Selection: Identify the audio sources that will be distributed throughout the facility, such as background music, paging systems, or audiovisual content. Choose audio sources that align with the intended use of each zone and ensure compatibility with the distributed audio system’s input options.
- Speaker Selection and Placement: Select speakers that are suitable for the intended application and environment. Consider factors such as speaker type (ceiling, wall-mounted, pendant), power handling, dispersion pattern, and aesthetics when choosing speakers for each zone. Ensure proper speaker placement to achieve balanced coverage and minimize sound overlap or interference between adjacent zones.
- Amplification and Signal Distribution: Choose amplifiers and signal distribution equipment that can accommodate the needs of a distributed audio system. Consider factors such as power output, impedance matching, and signal routing capabilities when selecting amplifiers and distribution equipment to ensure reliable performance and seamless integration with audio sources and speakers.
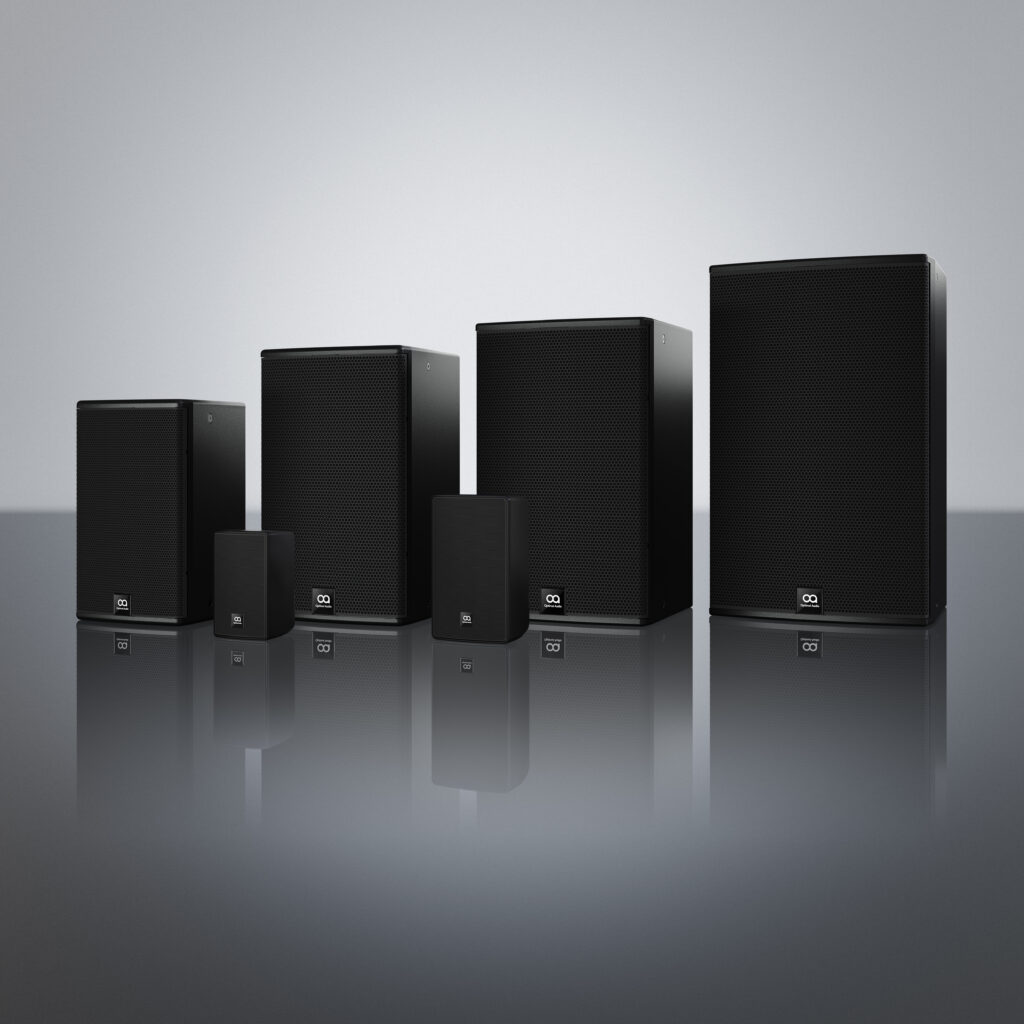

Installation Tips and Best Practices:
When installing a distributed audio system in a commercial environment, adhere to the following tips and best practices:
- Professional Installation: Hire experienced audio professionals or integrators to design and install the distributed audio system. Professional installers have the expertise and resources to ensure proper system design, equipment selection, and installation, resulting in optimal performance and reliability.
- Proper Wiring and Cable Management: Use high-quality cables and connectors for audio signal transmission and power distribution. Properly route and label cables to minimise interference, signal loss, and potential hazards. Implement cable management solutions to organize and protect cables for easy maintenance and troubleshooting.
- System Calibration and Tuning: After installation, calibrate and tune the distributed audio system to optimise sound quality and performance. Adjust volume levels, equalisation settings, and speaker configurations to achieve balanced sound reproduction and consistent coverage across all zones. Regularly monitor and fine-tune the system as needed to maintain optimal performance over time.
- Testing and Commissioning: Thoroughly test and commission the distributed audio system before finalising installation. Verify proper operation of all audio sources, amplifiers, speakers, and control interfaces. Conduct comprehensive system testing and performance verification to identify and resolve any issues or discrepancies before handing over the system to the end-user.
In conclusion, distributed audio systems offer numerous benefits for commercial applications, including flexibility, scalability, enhanced coverage, and centralised control. By carefully considering design considerations, installation tips, and best practices, businesses can harness the power of distributed audio systems to achieve seamless integration and optimal performance in their facilities. Whether designing a distributed audio system for retail stores, corporate offices, hospitality venues, or educational institutions, prioritising proper planning, professional installation, and thorough testing is essential to ensure a successful outcome and a superior audio experience for all stakeholders involved.
Optimal Audio offers a one stop shop solution of controllers, amplifiers and loudspeakers, all working seamlessly together and operated easily thanks to the multi-award winning WebApp, and designed specifically for small to medium sized multi-zoned commercial installations.
